Real time systems issues
Real time systems issues
- Resource management issues
Scheduling
- Assign time slots (where and when to execute)
- Objective - have tasks meet deadlines
- 2 types: static and dynamic scheduling
- Static
- Uses tables
- reduces run time problems
- not very good at adapting to problems
- Also you must store a table that can take valuable memory
- The table needs to the length of the least common multiple of all of the tasks (this can get quite long)
- This can get very large if the tasks are relatively prime
- Priority
- uses priority from offline setup
- More adaptable, however requires scheduling during run time
- This can also allow you to reclaim unused compute time
- Uses tables
- Dynamic
- Planning based
- does scheduling online and checks if it works on line
- Best Effort (not great because no guarantee)
- uses other scheduling from OS class like FIFO and round robin
- Planning based
- Steps for scheduling
- check if task is doable
- For static systems this can be done before runtime with a table
- construct schedule
- for static systems, we can make a table that shows when all tasks are being done and store it in the memory before run time
Preemptive scheduling
- for static systems, we can make a table that shows when all tasks are being done and store it in the memory before run time
- check if task is doable
- Static
- You may want to pause a task low priority task for a higher priority task
- tends to allow more scalability (more tasks scheduled per compute time)
- Increases overhead in context switching so we want as few context switches as possible
Non preemptive scheduling
- Once task starts it will finish
- lower schedulability
- lower overhead due to no context switching
- used more in multiprocessor systems
Optimal Scheduling
- static scheduling
- optimal if for any set of tasks it always produces a feasible schedule when any other algorithm is able to
- Dynamic scheduling
- optimal if always produces a feasible schedule whenever a static algorithm with complete knowledge of all the possible tasks could do so
Priority driven preemptive scheduling
- Rate monotonic system is priority based system
- This system only deals with periodic tasks, no support for a-periodic tasks
- The task with the shortest period has the highest priority
What is needed in real time scheduling algorithm
- fault tolerance
- resource reclamation
- communications
- Computer arch issues
- computing subsystems
- communication systems
- I/O sub systems
- Every system must have real time grantees or the whole system does not meet it
- Software issues
- Regular logic requirements
Testing for schedulability
- Critical zone theorem
- States that if every task of a higher priority level is started at the same time as a task x and x is able to complete, you are able to know that no mater what, task x is able to be completed
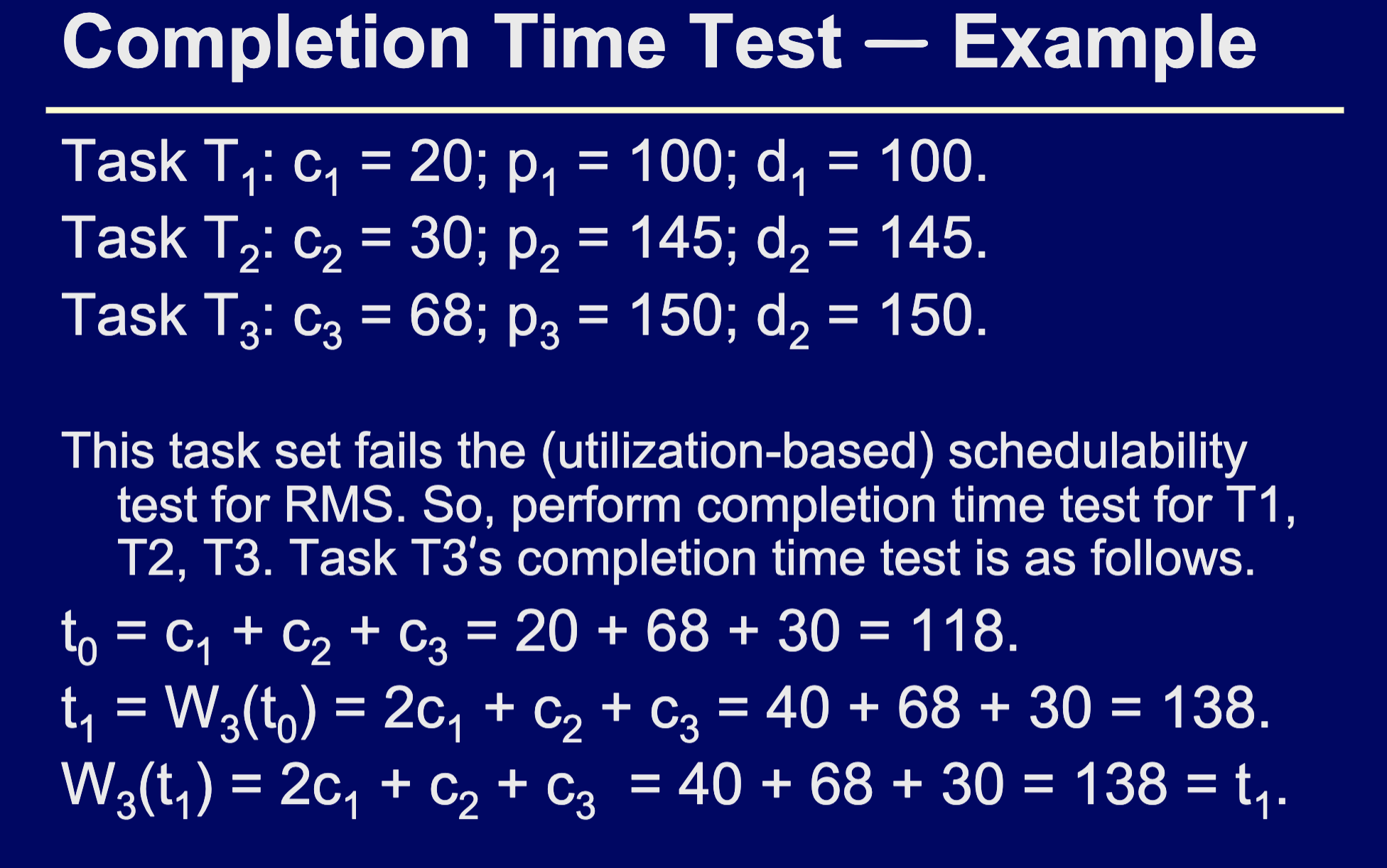
- Completion time test
- add up the time to execute every task and add in if tasks have to be executed multiple times. Then add in the time to complete the task you are evaluating, if all of these combined sum up to less then the deadline for the task, it can be executed
- Do this for every task, normally start at the lowest priority task
- If every task passes this test, this condition is necessary and sufficient to be schedulable
- Example
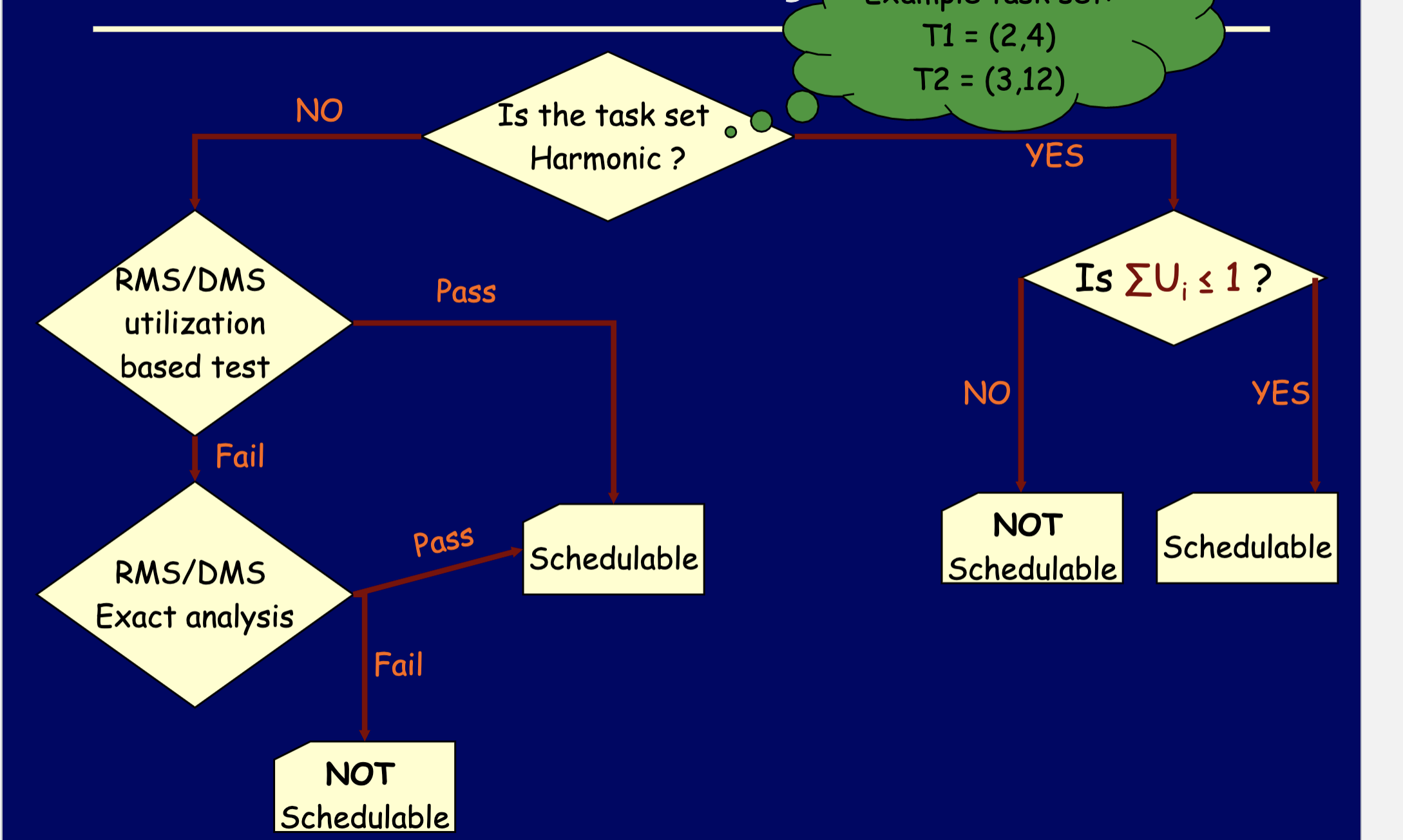
Generalized flowchart for if something is schedulable:
v1